The role of Acoustic guitars in large music ensembles was limited to one of support only. Electric guitars changed all that and earned tremendous popularity because of their ability to produce louder volume with distortion and richness in tone. So much so, that in present times it is difficult to comprehend any worthwhile soundtrack without electric guitars playing the tune.
Hence it is very essential to understand the basic underlying principles defining their functionality and produced sound. This will further help you in understanding the basic differences and finer details of various types of electric guitars and their sounds. Let us start with basic principles of Physics governing their functionality
Laws Of Electromagnetic Induction.
The functioning of any electric guitar depends on a very basic law of physics, known as the principle of electromagnetism. If you want to be more specific, it is the law of electromagnetic induction. According to this law:
- Change in electric field generates magnetic field or magnetism. Passing a varying electric current through an electric coil results in a magnetic field around it. The strength of this magnetic field depends on the value of electric current passes and the complete arrangement is known as an electromagnet.
- Also, a change in the magnetic field generates an electric current.
Hence, we can say that electricity and magnetism are related to each other and are different aspects of a single phenomenon known as electromagnetism. Change in either electric or magnetic field results in generation or induction of the other quantity. Hence, the name electromagnetic induction.
Electromagnetism Applied To Electric Guitars
By now, you will be curious to know, how the laws of electromagnetism are related to the functioning of the electric guitars. Let us have a look at the related phenomenon.
The main parts of the electric guitar involved in the generation and processing of electrical signals are:
- Magnetic pickups
- Volume and tone knobs
- Pickup selector switches
- Amplifier
- Tremolo bars
electric signals Generation based on string vibrations.
- Every electric guitar uses some kind of pickup to produce sound. Every pickup has one or more small bar magnets, to generate a magnetic field around it.
- The pickups of an electric guitar have pole pieces on top. The number of pole pieces is equal to the number of strings on the guitar. These pieces are used to direct the magnetic field into the string. These pole pieces can be magnets by themselves or be just metal pieces used in conjunction with the magnets. Their function is to magnetize the guitar strings.
- These bar magnets are wrapped around by thousands of turns of very thin wire coil made of copper. The very act of playing the guitar by the player results in the vibration of the strings. The magnetized strings in vibrating conditions create a varying magnetic field around the pickup. This varying, external magnetic field induces a voltage in the thin wire coil through the process of electromagnetic induction explained above.
- The induced voltage results in flow of current through the pickup coils to the electrical circuit of the guitar. This electrical circuit consists of volume and tone knobs, pickup selector switches and the amplifier.
- The amplifier is used to boost this current signal before sending it to the loudspeakers.
- If the string vibrates at 400 Hz frequency, it will induce a current of 400 Hz in the pickup.
In the previous section, we have seen how current signals are produced in an electric guitar on playing it. Now, we shall dive deep into various components that process these signals. Thus, these components either create or control the sound produced by an electric guitar.
Magnetic Pickups
Different types of pickups available for use in guitars are
- Contact pickups (these are essentially microphones)
- Active pickups (Require power source, like batteries)
- Piezoelectric pickups (usually placed inside the bridge and converts the actual vibration of string to electrical signals. Normally used for nylon string guitars, which can’t work on magnetic fields
- Magnetic or passive pickups
Out of the above list, magnetic pickups are the most commonly used ones. Active pickups are now slowly gaining popularity. Hence, we will focus on magnetic pickups in our ongoing discussion.
Magnetic pickup can be in the form of one big magnet or six separate pieces. These are then placed in a bobbin and are wrapped around by 8000 to 10,000 turns of fine copper wire.
Some pickups make use of screws as pole pieces. With this arrangement, the height of the screw and hence the distance to the string can be adjusted. The lesser the distance between the two, the stronger the current signal generated.
The creation of an electrical signal by the pickup coils was explained in the previous section. These single-coils act as an antenna for all types of electromagnetic energy in their vicinity. They can pick up undesired signals from sources such as computers, appliances, and even the guitar amps processing their own signals. These unwanted signals manifest themselves as a humming sound.
Different Magnets Used In Magnetic Pickups
Common types of magnets available for use are
- Ceramic magnets – Inexpensive, magnetically weak, and brittle
- Aluminium Nickel Cobalt – Inexpensive
- Samarian Cobalt – Expensive but magnetically strong
- Neodymium Boron Iron – expensive but magnetically strongest.
In the selection of magnets for pickups, there is always a trade-off between the strength of the magnetic and its cost. A stronger magnet requires a lesser number of turns in the coil for the same output. This results in a smaller pickup size also.
However, stronger magnets are more expensive. An aluminum nickel-cobalt magnet is most commonly used as it provides a good balance between cost and strength.
As the steel strings are ferromagnetic in nature, they experience a large attractive force in case of strong magnets. These strong magnets can also affect the vibration of the strings. The purpose of the pickup is to sense the vibrations only and not affect them in any way.
If you are using a strong magnet, it has to be made in a much smaller size, resulting in a concentrated magnetic field. Weaker magnets, on the other hand, are much larger in diameter. But they produce a broader magnetic field, more tolerant to the movement of strings.
Different Types Of Pickups
Single Coil Pickups
The pickup arrangement that we have discussed so far is essentially a single-coil pickup. Fender Telecaster was the first mass-produced guitar and had single-coil pickups on it. Single coil pickups were very successful and are still used by blues and country musicians. The reason they are still used is that they have brighter, crisper sound with greater note definition between strings
As already explained earlier, these pickups are prone to unwanted noise signals or “hums”. So, another type of pickup to overcome the problem got engineered. These included humbucking and Split coil pickups.
Humbucking Pickups Or Humbucker
Humbucker, as the name suggests, is a pickup designed and utilized to ‘buck’ the hum. These types of pickups were first conceptualized by Seth Lover, who worked as an engineer at Gibson, in 1955.
They are a combination of two single-coil pickups, having
- Pole pieces with opposite magnetic polarity. This is usually achieved by placing a magnet in the middle of the pickup. Due to this arrangement, each guitar string produces an opposite current signal in the two coils.
- The coil is wired in series with opposing or out-of-phase coil connections. With this type of connection, the output of one coil is entering the other, and the current flows in opposite direction from one coil to another.
Such a connection between the coils, flips
- the opposing guitar signals in the coils, bringing them in phase with each other. Hence, the signal gets doubled from its original single-coil pickup value.
- the unwanted noise signal, out of phase with each other. These two signals cancel each other, resulting in the termination of the hum.
Humbuckers or double coil pickups have a darker, louder, and heavier sound.
Effect Of Pickup Position On Tone
In order to fully understand the effect of the position of pickups on the tone of the sound produced, it is recommended to first understand the related characteristics of sound causing this effect.
Location Of Plucking And Overtones
Picking near the bridge, results in a “Twangy” sound, as against a “Brassy” sound on picking near the neck. We get different sounds by plucking the strings at different locations. Let us see why
For illustration purposes, let us see the impact of plucking a string in the middle and at 1/3rd length
- Middle: This results in an elimination of all the even harmonics because nodes of these harmonics are in the middle of the string. So, only the odd harmonics remain.
- At 1/3rd: All the harmonics, that are multiples of 3, are eliminated. Other harmonics remain.
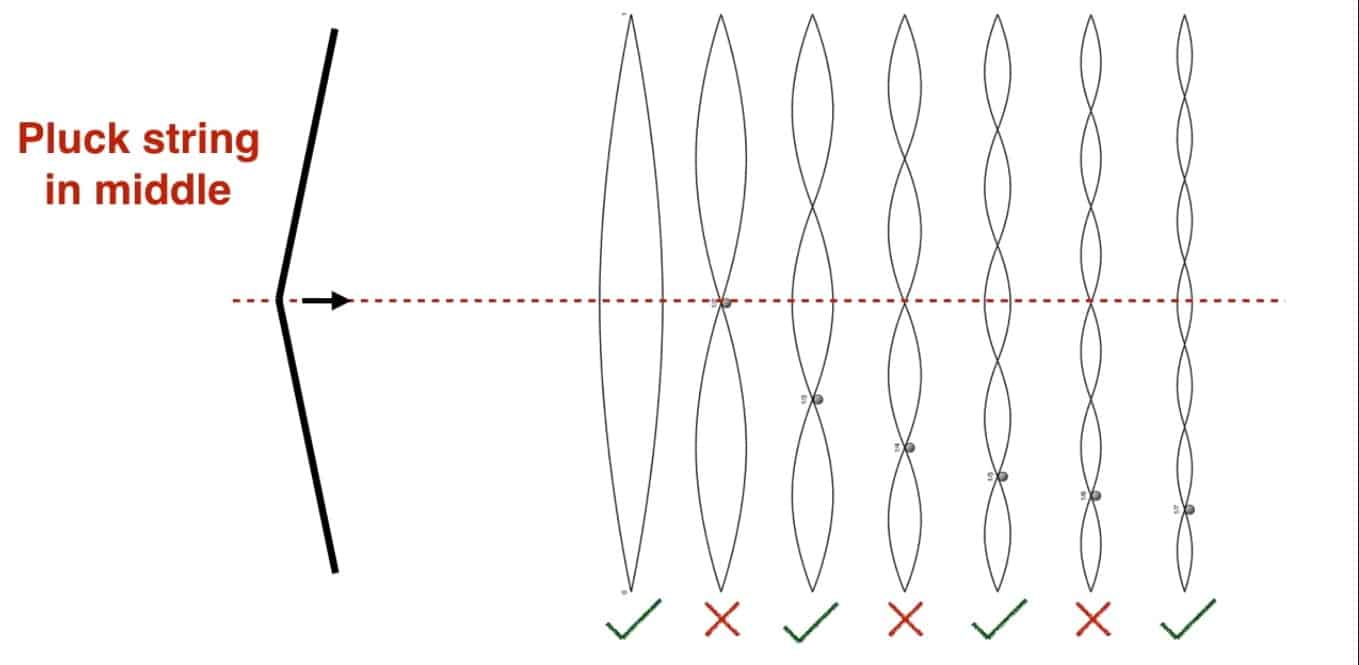
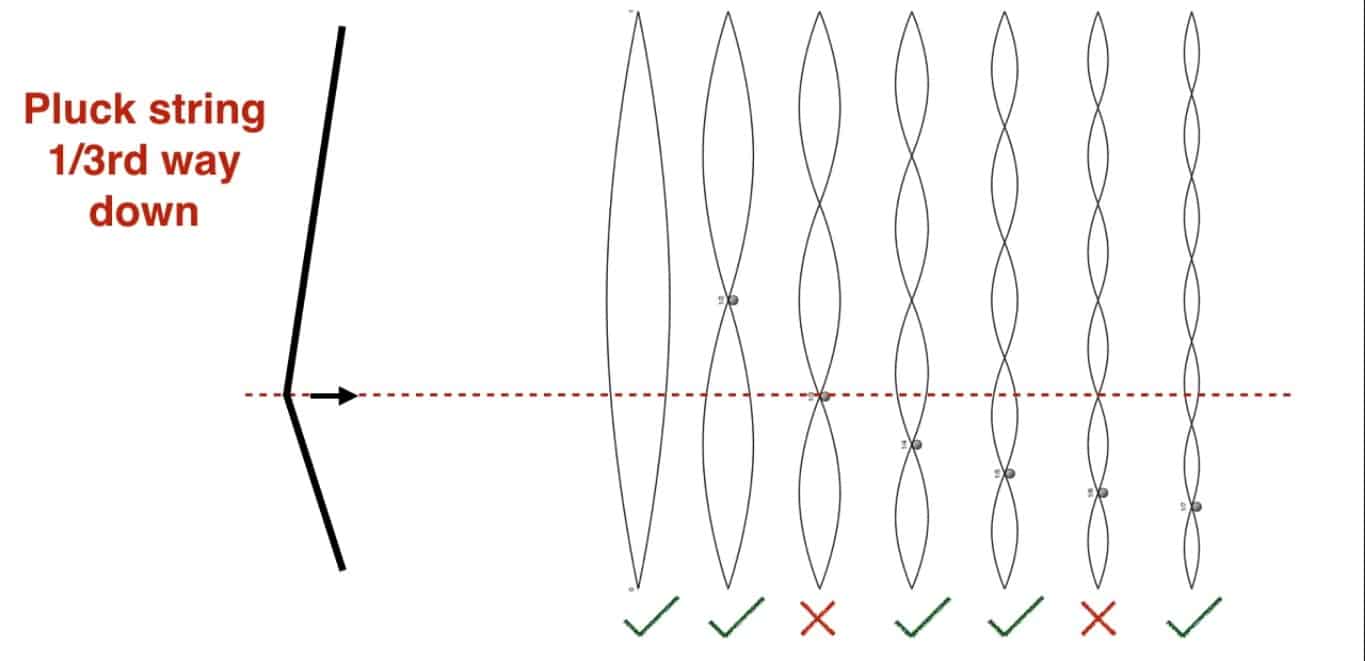
In the same way, the impact for other locations of picking can be determined. We conclude that plucking the strings at different locations results in different proportions of overtones or harmonics. Hence the different sounds.
Back To Pickups
With all the underlying principles fully understood, we are now ready to appreciate the impact of the location of the pickups on the sound tones.
Pickups only detect string vibrations that are near to them. If the node of any harmonic falls above the pickup, it will not sense that harmonic. In the same way, if the antinode of any harmonic, is above the pickup, it will form a major component of the sound produced. Hence, pickups effectively filter the harmonics, based on their locations. Hence different tonal sounds are picked up by them.
The majority of electric guitars have two pickups, near the bridge and the neck.
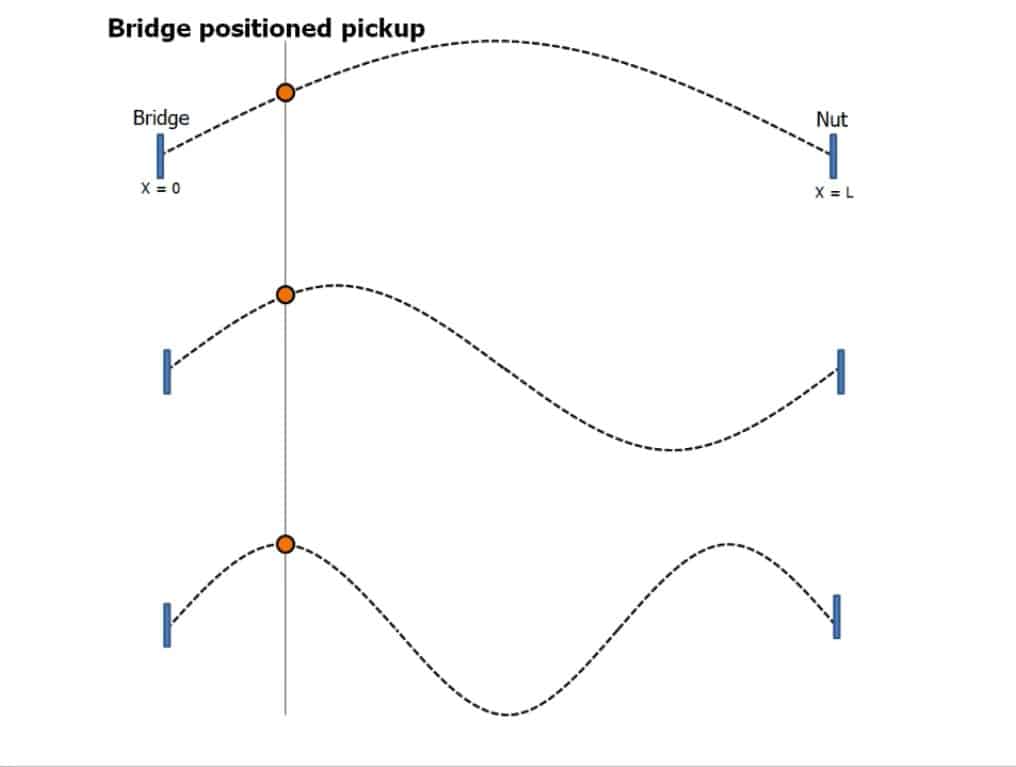
Pickup Near The Bridge.
Pickup placed close to the bridge is near the anchor point of the string.
- String vibrations do not contain a strong component (magnitude) of fundamental frequencies here. But, the magnitude of vibration of higher frequencies is much larger. From the image, you can see that magnitude of the third harmonic is much larger than the fundamental.
- An increased presence of higher harmonics results in a brighter tone.
- As the magnitude of string vibration is smaller near the bridge, the bridge pickup has more number of turns in the coil. This is done to make it more sensitive to small variations in the magnetic field.
- Due to more turns, the tone of the bridge pickup is more midrange and treble-heavy. Gibson even calls this “Treble” position on its pickup selector switch.
- Adjusting bridge pickup height to make it closer to the string, thereby picking more volume is also a common practice.
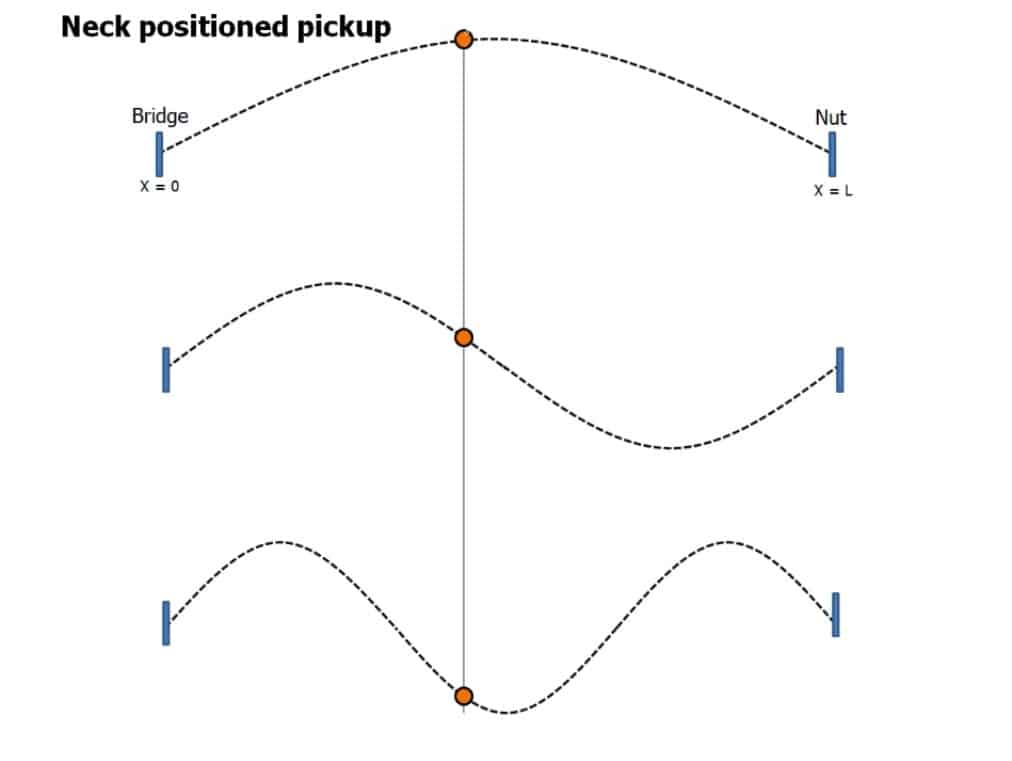
Pickup Near The Neck
This pickup senses more of the fundamental frequency in comparison to harmonics through it. Hence,
- It produces a much mellowed, clean, and pure tone that works well with the cords.
- It is called the “Rhythm” position on the pickup selector switches of many of Gibson’s popular guitars including Les Paul.
Middle Pickup
Some of the electric guitars, like the Fender Stratocaster and those influenced by it, have an additional middle pickup.
- The tone of this pickup is usually somewhere in the middle of the above two pickups. It is clearer than the neck pickup but not as bright as the bridge pickup. It has a much wider balance of harmonics.
- Origin Stratocaster had a three-way switch, to select either of the three pickups. Some of the players experimented, by sticking the switch in between the two settings. The result was an interesting combination of sound between the adjacent pickups, with a mellow tone, which became famous as “ Strat quack”.
- Fender officially introduced a 5-way switch, to incorporate these in-between positions in, the 1970s.
Volume And Tone Knobs
Electric guitars are provided with volume and tone controlling circuits which are used to process the signal before sending it to the amplifier. The circuits have one or more volume and tone control knobs. By adjusting these knobs, we can change how the guitar sounds.
With the volume control knob, we can make the guitar sound loud or soft. Tone control knobs act like a filter, through which we can eliminate certain frequencies. Below these knobs, there are potentiometers, to make these changes. In terms of looks, both the knobs are identical but differ in the way they are wired. These potentiometers generally come in two ranges – 250K ohms and 500K ohms.
A typical electrical circuit is shown below.
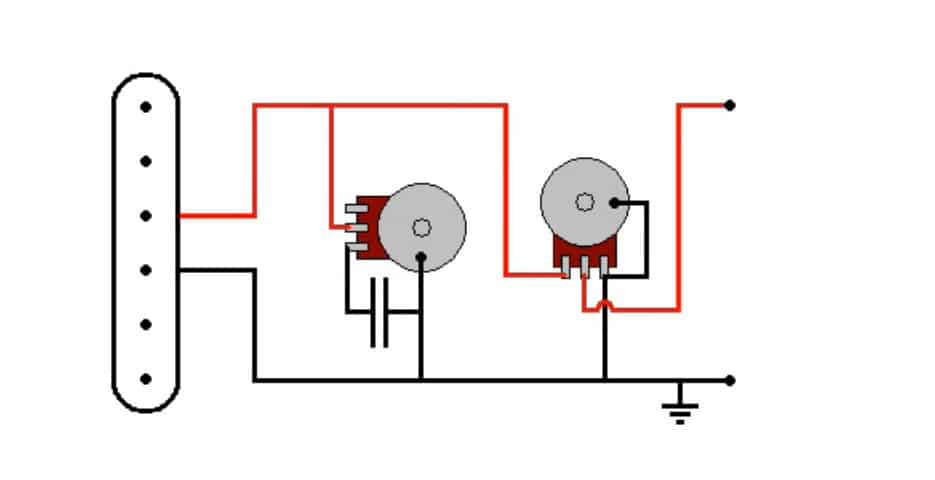
Volume Circuit
Part of the circuit shown on the right is the volume circuit. By adjusting the resistance of the potential, we can control the amplitude of the signal, to the Jack. From Jack, the signal goes to the amplifier and then to the Speaker.
Tone Circuit
Part of the circuit on the right side is the tone circuit. It has a capacitor of 0.022 microfarads to form a simple low pass filter. This filter will normally remove the higher frequencies and allows the lower frequencies to pass through. However, by adjusting the potential you can control the frequencies to filter.
Pickup Selector Switches
It allows the guitar player to select which pickup produces sound. It can be either neck or bridge pickup or a combination of both.
In, Stratocaster type of guitars, we have three pickups and a 5-way selector switch. We can select any one of the pickups or a combination of pickups.
Guitar Amplifier
In this section, we will briefly introduce you to the guitar amplifier, distortion, feedback, and important parts of the amp. We will discuss them in full-length in a separate article.
Distortion
Guitar amplifiers are quite different from stereo amplifiers. Stereo amplifiers have to reproduce and amplify the sound with minimal distortion possible. Guitar amplifiers can be called upon to either produce clean sound or with distortion. Guitar amplifier and loudspeaker together as one unit are often called Guitar Amp.
Guitar Amp is said to produce sound with distortion when the signal in its circuitry is too powerful for it. Sound with distortion is actually desired by the players and many of the available amplifiers have the ability to control the level of distortion.
Feedback Loops
If the level of sound coming out of the Guitar Amp is very loud, it can make the guitar strings to vibrate. In such a scenario, once the player has hit the note, the string will continue to vibrate for very long. This is known as a feedback loop between the amp and the guitar.
Parts Of Guitar Amp
The main parts of Guitar Amp are
- Pre-amplifier
- Power amplifier
- Speaker
Some guitar amps also have effects and reverb circuits before the power amplifier.
Power amplifiers require a certain minimum input signal level to function. Signals from the electrical circuits of the guitar do not have enough power to drive the power amplifiers. Hence a Pre-amplifier is used to boost the signal to levels required by the main amplifiers. It also reduces noise and interference in the guitar sound signals.
The majority of guitar power amplifiers still make use of vacuum tubes. The distortion patterns and the characteristics of the vacuum tubes are loved by most musicians.
Amplifier circuits are further classified as Class A, Class B, and Class AB, where there is a tradeoff between Crossover distortion and efficiency. But some musicians look for specific classes to get the exact sound they are desirous of.
Tremolo Bars
We had touched upon the dynamic characteristics like attack, decay, vibrato, and tremolo while discussing the timbre or quality of the sound. We will define it briefly here for you to be able to understand the functioning and purpose of tremolo bars.
Attack
Plucking of a guitar string results in a rapid increase in the peak amplitude of the vibrating guitar string. This phenomenon is known as an attack.
Decay
Once the guitar string is plucked and left, the vibration amplitude gradually decreases until it stops vibrating. This phenomenon is named the decay of vibrations.
Both attach and decay are demonstrated in the attached image.
Vibrato And Tremolo
Vibrato is defined as “periodic changes in the pitch of a tome” and is similar to Frequency Modulation or FM in communications.
Tremolo on the other hand is described as the “periodic changes in the loudness or the amplitude of the tone”. This is similar to Amplitude Modulation or AM.
Within reasonable limits, vibrato can be a desired characteristic of the human voice, as it can add expression and richness to it.
Back To Tremolo Bars
Fender marketed Stratocaster with a Tremolo arm or bar. While he named it a Tremolo arm, the attached bridge actually produces the vibrato effect, causing a lot of confusion in the guitar world.
In the assembly, there is a floating bridge resting on two numbers of face-mounted posts. The arrangement has two springs on the underside to keep it in place by proving the required counterforce. By applying pressure to the bar, the bridge can tilt either forward or in the backward direction, making strings loose or tight. As explained above, the pitch or frequency of the sound produced depends on the length, mass (thickness), or tension of the string.
An increase in tension of the string increases the pitch and a decrease reduces it.
Conclusion
We hope that this article on how an electric guitar works have provided you with sufficient initial insights into the functioning of electric guitars, pickups, and other electrical components. Also, you have been introduced to the impact of harmonics and dynamic characteristics on the quality of sound produced. Please comment if you have any clarifications or would like us to cover some more articles.
